Meditation has long been praised for its calming effects, but for many people, it still feels like something that requires hours of practice, deep discipline, or a complete lifestyle shift. That assumption is finally being challenged. New scientific findings show that 27 minutes of meditation may be enough to trigger measurable changes in the brain.

Not symbolic changes, not self-perceived improvements, but real neurological shifts that researchers can observe and measure. What makes this discovery so compelling is its simplicity. You don’t need years of experience or a strict daily routine. According to recent neuroscience research, 27 minutes of meditation can influence how the brain manages focus, stress, and emotional control. That’s a realistic amount of time for most people, which is exactly why this finding is gaining so much attention.
The concept that 27 minutes of meditation can lead to brain changes has reshaped how scientists think about mental training. In studies involving beginners with no meditation background, researchers observed noticeable shifts in brain activity after just one session. These changes were not abstract. They appeared in areas responsible for attention, emotional regulation, and stress processing. This challenges the old belief that meditation only works after months or years of practice. Instead, the brain seems ready to respond almost immediately when attention is directed intentionally. Short meditation sessions activate neural pathways linked to awareness and calm, showing that meditation is far more accessible than once believed.
Table of Contents
Just 27 Minutes of Meditation Can Create Measurable Changes in the Brain
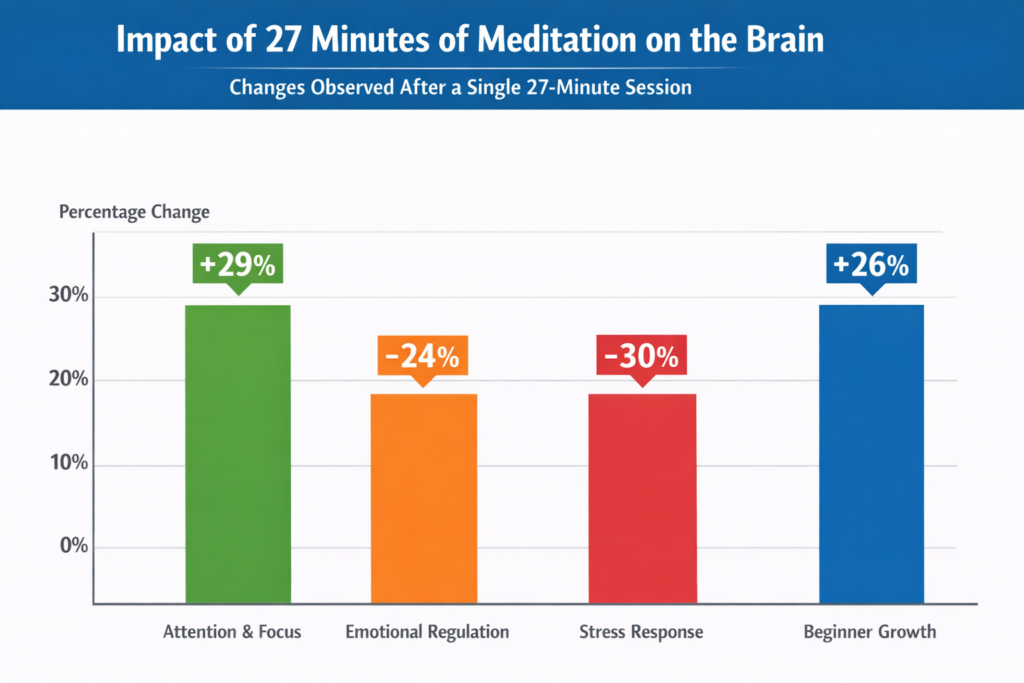
| Focus Area | Observation | Impact On The Brain |
|---|---|---|
| Session Duration | One 27-minute session | Immediate neural response |
| Attention Centers | Increased activity | Improved focus |
| Emotional Regulation | Reduced reactivity | Greater emotional balance |
| Stress Response | Lower stress signals | Calmer brain patterns |
| Experience Level | Beginners included | No prior practice required |
The discovery that 27 minutes of meditation can create measurable changes in the brain is a powerful reminder of how adaptable the human mind truly is. It proves that meaningful mental change doesn’t require extreme effort or long hours of practice. With a short, focused session, the brain begins reshaping how it handles focus, emotion, and stress.
The Science Behind Short Meditation Sessions
The human brain is highly adaptable. This adaptability, known as neuroplasticity, allows neural connections to strengthen or weaken based on use. Meditation works by engaging this natural process. When you meditate, you repeatedly bring your attention back to a chosen focus, such as your breath or bodily sensations. During 27 minutes of meditation, the brain begins adjusting how different regions communicate. Focus-related networks become more active, while stress-related circuits quiet down. What surprised researchers most was how quickly these changes appeared. Instead of slow progress over weeks, measurable shifts occurred almost immediately.
Changes In Attention And Focus
One of the most consistent effects of meditation is improved attention. Meditation trains the brain to notice distractions and gently return focus. This repeated action strengthens neural networks responsible for sustained attention. After short meditation sessions, participants performed better on attention-based tasks. Brain activity showed stronger engagement in regions linked to concentration and reduced activation in areas associated with mental wandering. This explains why many people report feeling clearer and more focused after 27 minutes of meditation, even without prior experience.
Emotional Regulation and Calm
Meditation also changes how the brain processes emotions. Instead of reacting automatically to thoughts or feelings, meditation encourages observation without judgment. This practice affects emotional control centers in the brain. Research shows that 27 minutes of meditation can reduce activity in areas linked to emotional reactivity while increasing activity in regions associated with awareness and balance. This shift allows individuals to respond more thoughtfully to emotional triggers rather than reacting impulsively.
Stress Reduction at the Neural Level
Stress leaves a clear mark on the brain. Prolonged stress keeps certain neural circuits in a constant state of alert, which can lead to fatigue, anxiety, and burnout. Meditation interrupts this pattern. After a short meditation session, researchers observed reduced stress-related signaling in the brain. This means meditation doesn’t just help people feel relaxed temporarily. It actually changes how the brain processes stress, potentially protecting it from long-term damage caused by chronic pressure.
Why Beginners Experience Fast Results
One of the most encouraging aspects of this research is how quickly beginners respond. Participants did not need prior meditation experience to see changes. This suggests that attention and awareness are natural brain functions, not advanced skills that take years to develop. The brain already knows how to focus and observe. Meditation simply strengthens those existing abilities. That’s why 27 minutes of meditation can produce measurable results even for first-time practitioners.
Implications For Mental Health
These findings have significant implications for mental health support. Time is one of the biggest barriers preventing people from trying meditation. Knowing that 27 minutes of meditation can make a difference removes that obstacle. Mental health professionals are increasingly exploring short meditation practices as tools for managing stress, anxiety, and focus-related challenges. Because the brain responds quickly, meditation can offer immediate support rather than delayed benefits.
Practical Benefits In Daily Life
- The impact of short meditation sessions extends beyond mental health. Improved focus can enhance productivity, emotional regulation can improve relationships, and reduced stress can support overall well-being.
- Because the time commitment is small, meditation becomes easier to fit into daily routines. A single session in the morning, during a break, or before sleep can influence how the brain functions throughout the day.
How This Research Changes The Perception Of Meditation
- For a long time, meditation was viewed as a slow, long-term practice with benefits that took years to appear. This research changes that narrative. It shows that meditation can produce fast, measurable results.
- By framing meditation as efficient and practical, science has made it more approachable. 27 minutes of meditation is no longer a spiritual goal but a scientifically supported form of mental training.
The Role Of Consistency Over Time
- While a single session can create changes, consistency still matters. Repeating short meditation sessions strengthens the neural pathways activated during practice. Over time, these changes become more stable and long-lasting.
- However, the key takeaway remains clear. You don’t need to start with long sessions. Even brief, consistent practice can build meaningful improvements in brain function.
Meditation As A Cognitive Skill
- Meditation is increasingly being recognized as a cognitive skill rather than a relaxation technique. Like physical exercise strengthens muscles, meditation strengthens attention, awareness, and emotional control.
- Short sessions prove that this skill can be developed efficiently. 27 minutes of meditation acts as a mental workout that engages multiple brain systems at once.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
- Many people believe meditation requires silence, perfect focus, or a calm mind. In reality, meditation works even when the mind wanders. The act of noticing distraction and returning attention is what trains the brain.
- This understanding helps beginners feel less discouraged. Meditation isn’t about doing it perfectly. It’s about practicing awareness, even for a short time.
This research makes meditation more accessible than ever. Whether you’re new to the practice or simply short on time, 27 minutes of meditation offers a realistic and science-backed way to support brain health and mental clarity in everyday life.
FAQs on 27 Minutes of Meditation
How Long Should I Meditate to See Brain Changes
Research suggests that 27 minutes of meditation can already lead to measurable changes in brain activity.
Do I Need to Meditate Every Day
Daily practice helps long-term benefits, but even occasional sessions can positively affect brain function.
What Type of Meditation Works Best
Mindfulness-based practices that focus on breath or present-moment awareness are commonly used in studies.
Can Meditation Help with Stress and Anxiety
Yes, meditation reduces stress-related brain activity and supports emotional regulation.
















