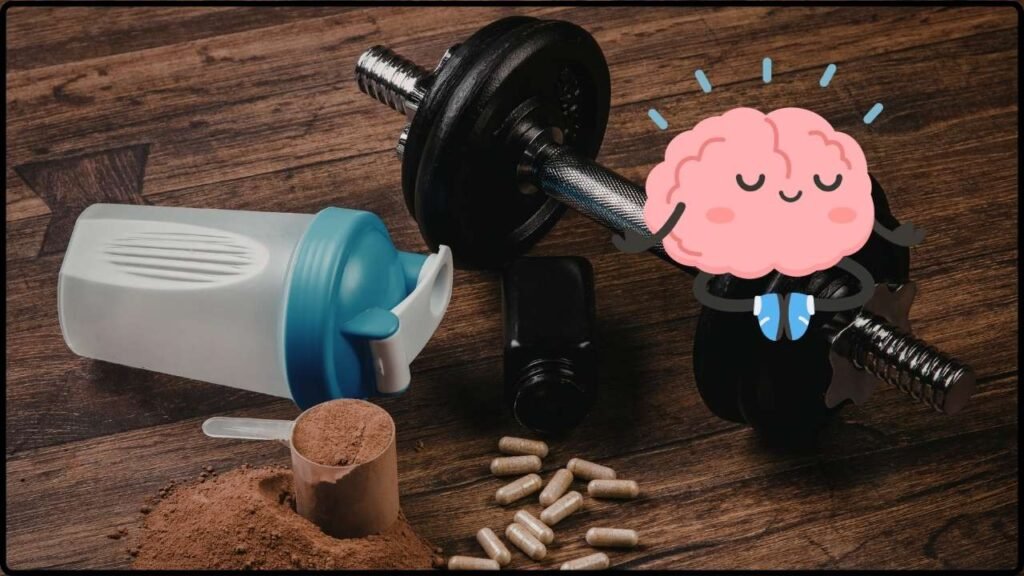
A Common Workout Supplement May Aid Brain Health: If you’ve ever mixed a scoop of creatine into your protein shake, chances are you were doing it to crush your gym session—not to sharpen your memory or boost your focus. But here’s the twist: a growing stack of research now suggests creatine may aid brain health, too. That’s right. This tried-and-true workout supplement is stepping into a whole new spotlight. It’s not just helping bodybuilders and athletes—it might just be your brain’s secret weapon for fighting fatigue, boosting clarity, and even tackling depression. Let’s break it all down in plain English (with some science sprinkled in).
Table of Contents
A Common Workout Supplement May Aid Brain Health
Creatine is no longer just for gym bros and athletes. With mounting evidence supporting its role in cognitive function, mental clarity, and mood enhancement, it may be the most underrated brain supplement out there. It’s safe, affordable, accessible, and backed by science—not just hype. Whether you’re an overworked student, a burned-out parent, or just someone looking to think sharper and feel better, creatine might be worth a spot in your daily routine. Just don’t forget to stay hydrated—and maybe pass some along to your brain as well as your biceps.
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Supplement Studied | Creatine |
| Main Benefit Found | May reduce mental fatigue, improve reaction time, and support mood health, even in sleep-deprived individuals |
| Study Focus | 3–5 grams of creatine daily improved attention, mental clarity, and reduced depressive symptoms |
| Emerging Mental Health Use | A 2024 study in India found creatine helped participants with moderate-to-severe depression reduce symptoms significantly |
| Expert Insight | Dr. Vernon Williams: “May help mitigate cognitive decline related to fatigue and stress.” |
| Safety Profile | Safe for healthy adults with minimal side effects (bloating, mild GI upset); widely used by 1 in 4 U.S. adults |
| Recommended Dose | 3–5 grams daily; no loading phase required |
| Official Resource | NIH: Creatine Fact Sheet |
What Is Creatine and Why Is It So Popular?
Creatine is a substance found naturally in your body. It’s mostly stored in your muscles but also found in your brain, where it helps produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate)—your cells’ main source of energy.
You get creatine from foods like red meat and fish, but unless you eat a lot of those every day, you’re probably not maxing out your natural stores. That’s where supplements come in.
Creatine monohydrate—easily the most researched form—is cheap, accessible, and a staple in almost every athlete’s pantry. But now researchers are discovering that creatine could be more than muscle-deep.
Creatine and the Brain: A Common Workout Supplement May Aid Brain Health
So why would a fitness supplement help your brain?
Think of your brain as a 24/7 engine—it runs non-stop, even while you sleep. It uses 20% of your body’s energy, and under stress (like lack of sleep or mental overload), that energy gets drained fast.
Creatine helps recycle and replenish ATP, keeping your brain’s energy levels up. That translates into sharper thinking, faster reaction times, and less mental fatigue.
In a 2023 study published in Psychopharmacology, researchers tested this out by giving participants 3 grams of creatine daily for 6 weeks, while subjecting them to partial sleep deprivation.
The results?
- Faster decision-making
- Better cognitive flexibility
- Reduced sleep-related fog
- Improved reaction time
Translation: Creatine gave their tired brains a second wind.
Real-World Scenario: Sleep-Deprived Students and Night Shift Workers
You don’t have to be a pro athlete to benefit. Ever pulled an all-nighter? Worked back-to-back shifts? Juggled parenting and a demanding job?
Creatine might help recharge your mental battery when you’re drained.
In fact, a 2021 systematic review in Nutrients concluded that creatine helps improve short-term memory, mental fatigue, and processing speed—especially in individuals who are under cognitive stress, like students and night shift workers.
A Surprising New Benefit: Depression Support
Here’s where things get even more interesting.
A 2024 study from India, published in Psychiatry Research, explored creatine’s effects on major depressive disorder (MDD). The researchers wanted to see if adding creatine to standard therapy (like talk therapy or SSRIs) would lead to better results.
The findings:
- Participants who took 5g of creatine daily for 8 weeks showed significant reductions in depressive symptoms compared to placebo.
- They reported better sleep, energy, and mood stability.
- 11 patients in the creatine group reached remission, compared to 5 in the placebo group.
“Creatine could offer a low-cost, widely available mental health boost,” said Dr. Riccardo De Giorgi, co-author of the study. “It holds promise especially in low-resource or underserved settings.”
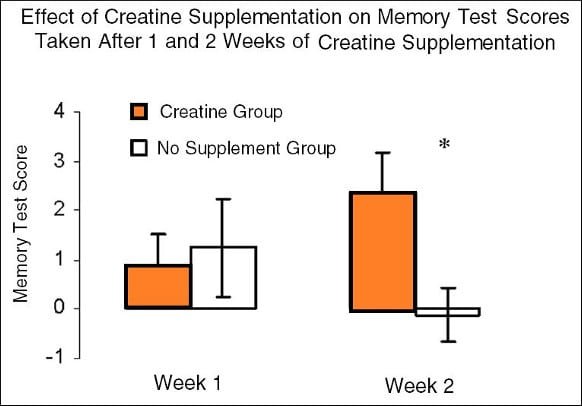
How Creatine May Help Mood?
Creatine affects the energy metabolism in brain cells, particularly in areas like the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, which play key roles in emotion regulation and memory.
A 2012 pilot study from the University of Utah also found that creatine supplementation improved depressive symptoms within two weeks in women already taking antidepressants.
The idea is that by enhancing cellular energy, creatine may help the brain function more efficiently, even when neurotransmitters like serotonin are out of balance.
A Practical Guide: How to Take Creatine for Brain Health
Which Form to Choose?
- Stick with creatine monohydrate
- Look for products with third-party testing (like NSF Certified or Informed Choice)
Dosage
- 3–5 grams per day is ideal for cognitive and mood benefits
- No need for a “loading phase” (which is common in bodybuilding)
Timing
- You can take it any time of day
- It’s OK with or without food
- Mix into water, smoothies, or coffee
Consistency
- Daily use is key—it may take 2–3 weeks to notice benefits
- Store in a cool, dry place for max shelf life
Safety and Side Effects: Is Creatine Risky?
Creatine is considered one of the safest and most studied supplements on the market.
According to the NIH, it’s safe for long-term use in healthy adults.
Possible (but uncommon) side effects:
- Mild bloating
- Water retention
- Upset stomach (rare—try smaller doses if this happens)
Drink extra water to stay hydrated, especially if you’re physically active.
Important: If you have kidney disease, diabetes, or take diuretics, talk to your doctor before starting.
Creatine vs. Nootropics: How It Stacks Up
“Nootropics” are brain-boosting supplements like L-theanine, ginkgo biloba, and modafinil. While many claim to improve focus, few have strong scientific backing.
Creatine, on the other hand, is one of the few cognitive enhancers with decades of clinical research supporting its safety and effectiveness.
It may not give you instant focus like caffeine, but it supports long-term mental resilience, especially under stress.
What Experts Are Saying About A Common Workout Supplement May Aid Brain Health?
“Creatine is like a battery charger for your brain,” says Dr. W. Christopher Winter, a neurologist and sleep expert. “Especially if you’re running on low sleep or feeling burnt out.”
“It’s one of the most underutilized supplements in mental health,” adds Dr. Drew Ramsey, a nutritional psychiatrist at Columbia University. “Creatine supports both brain energy and neuroplasticity.”
Even pro athletes like LeBron James, Simone Biles, and Serena Williams have reportedly used creatine—not just for muscles, but for recovery and focus.
Experts Say a Popular Classic Cream May Show Noticeable Skin Changes in Two Weeks
Why a Rare Neurological Condition Makes This Woman See Faces as Dragons
The Chronovisor Story — The Alleged Vatican Device Said to View the Past
















