Robotaxis Expand in the U.S.: In the ever-evolving landscape of transportation, robotaxis — self-driving cars that pick you up and drop you off — are no longer just a sci-fi fantasy. They’re rolling out in real cities across the United States. From Waymo’s driverless rides in Phoenix and San Francisco to Uber’s new partnerships with autonomous vehicle startups, the robotaxi boom is here, and it’s racing ahead at full throttle. Whether you’re a tech-savvy kid curious about robot cars or a professional keeping an eye on the future of mobility, there’s a lot happening — and fast. This article dives deep into how robotaxis are expanding in the U.S., why it matters, and what to expect next.
Table of Contents
Robotaxis Expand in the U.S.
Robotaxis are no longer science fiction — they’re a present-day reality reshaping how Americans get around. From Silicon Valley to the Sun Belt, self-driving services are expanding rapidly, driven by tech innovation, investor money, and real public demand. While trust, regulation, and infrastructure still pose hurdles, the momentum is undeniable. Whether you’re riding in one, building the tech behind it, or investing in the future of transportation — robotaxis are changing the game.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Leading Players | Waymo, Uber, Tesla, Waabi, Zoox |
| Market Value | Waymo valued at $126B |
| Operating Cities | Phoenix, San Francisco, Austin, Los Angeles, Nashville |
| Major Partnerships | Uber + Waabi: 25,000 robotaxis planned |
| Investment Surge | $55B+ invested globally in AVs |
| U.S. Regulations | Vary by city/state; safety still under review |
| Global Competition | China, UAE, EU also scaling robotaxi fleets |
| Official Info | Waymo Official Site |
What Are Robotaxis, and Why Should You Care?
Let’s break it down — robotaxis are self-driving cars that work like Ubers or Lyfts, but without a human driver. You tap a button, and boom — a car shows up, drives you where you need to go, and no one’s behind the wheel.
This might sound like something out of Back to the Future, but it’s happening now. In fact, Waymo, Uber, and Tesla are already deploying these vehicles in major U.S. cities.
But why does this matter? Because robotaxis are set to revolutionize:
- Urban mobility: Traffic, parking, and congestion could ease
- Safety: Removing human error (behind 94% of crashes, per NHTSA)
- Accessibility: Helping seniors, people with disabilities, and kids get around
- Jobs: While driver roles may shift, new tech jobs are emerging in AV support and development
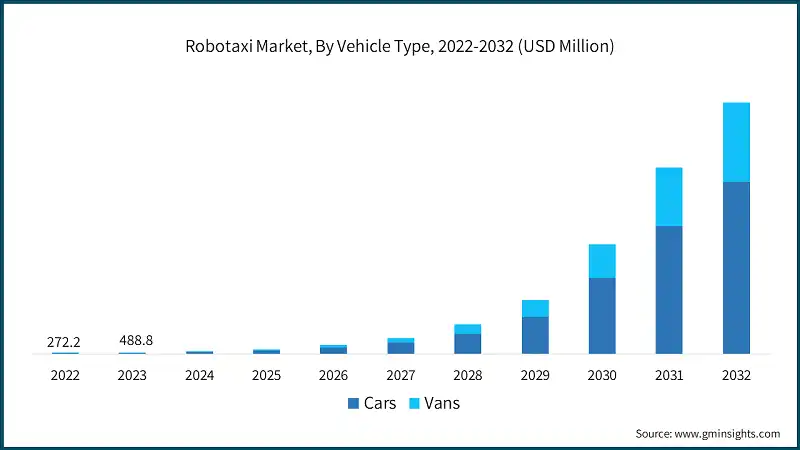
Robotaxis Expand in the U.S.: Who’s Driving the Robotaxi Race?
Waymo: The Veteran and Industry Leader
Waymo, owned by Alphabet (Google’s parent company), is the undisputed leader in U.S. robotaxis. They’ve logged over 20 million real-world miles and now operate in cities like Phoenix, San Francisco, and Nashville — with fully driverless service.
Their fleet consists of Chrysler Pacifica minivans and Jaguar I-Pace EVs, both retrofitted with sensors, lidar, and radar arrays. Waymo raised $16 billion in 2026 to expand, and it’s now valued at $126 billion, outpacing legacy automakers.
Uber + Waabi: An AI-Powered Partnership
Uber’s strategy is more about platform integration. Instead of building its own cars, Uber is teaming up with companies like Waabi — a startup that raised $1B to roll out 25,000 robotaxis in the next few years.
Waabi focuses on AI-first simulation training, speeding up development and safety testing. Uber has already integrated AVs in Dallas, Austin, Phoenix, and parts of Los Angeles.
Tesla: The Autonomous Disruptor
Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) software is currently Level 2 or 3 autonomy, meaning a human must be present — for now. Elon Musk claims a dedicated Tesla Robotaxi is on the way, and it’s expected to be a sleek, driverless vehicle with no pedals or steering wheel.
Despite delays, Tesla has logged billions of miles in Autopilot and FSD mode, giving it a vast data advantage.
Zoox, Cruise, and Others
- Zoox, Amazon’s AV company, has designed a symmetrical, bi-directional robotaxi for dense urban streets. It’s already testing in Las Vegas and San Francisco.
- Cruise, backed by GM, was offering rides in San Francisco before a crash halted operations in 2023. They’re expected to return soon with updated safety protocols.
Real-World Stats and Milestones
- 94% of serious U.S. crashes are due to human error (NHTSA)
- Waymo and Cruise combined have driven over 30 million miles
- Robotaxi market expected to reach $327 billion globally by 2030
- AV testing is underway in over 15 U.S. states
Robotaxis Expand in the U.S.: How to Ride a Robotaxi (Step-by-Step Guide)
- Download the App (Waymo, Uber, or Cruise)
- Enter Pickup Location – Must be inside the service zone
- Request a Ride – Choose “Autonomous” if available
- Unlock Car with App – No driver means you open it yourself
- Buckle Up and Enjoy the Ride – Sensors and software guide the trip
Example: In Phoenix, you can ride Waymo with no human backup. The car will navigate intersections, traffic, and drop you off at your destination — all on its own.

Insurance, Liability, and Legal Questions
A big question still hanging in the air: Who’s responsible in a crash?
- If a robotaxi hits another car, is it the manufacturer, the software provider, or fleet operator who’s liable?
- States like California, Texas, and Arizona are working on legislation, but there’s no federal AV law yet.
- Many robotaxi operators hold special commercial AV insurance with strict data logging.
For legal professionals and businesses, this is a huge space to watch. Regulations could determine whether AV adoption speeds up or stalls.
Public Trust and Safety Concerns
According to AAA’s annual autonomous vehicle survey (2023):
- 68% of Americans are hesitant to ride in fully self-driving vehicles
- Only 9% fully trust the technology
Robotaxi companies are countering this with:
- Transparent safety data reports
- In-car cameras for two-way monitoring
- Redundant backup systems (brakes, steering, CPUs)
Still, building trust will take time — and a few million more safe miles.
Rural America and the Robotaxi Gap
While cities like San Francisco, Los Angeles, and Austin are hotspots for AVs, rural areas remain underserved.
Challenges include:
- Sparse HD mapping
- Lack of 5G coverage
- Weather variations (snow, fog, unmarked roads)
However, experts believe rural deployments will happen later through delivery AVs and shuttle services for towns with aging populations.
Global Competition: U.S. vs China vs Europe
While the U.S. dominates early robotaxi rollout, China is gaining ground fast:
- Baidu’s Apollo Go is already live in over 10 cities, including Beijing and Wuhan
- WeRide and Pony.ai are testing in the Middle East and Southeast Asia
- Europe is slower, due to tighter regulations, but Mercedes-Benz and Volkswagen are piloting robo-shuttles
This global race could affect export markets, technology standards, and economic power over the next decade.
Jobs and Workforce Impact
It’s true — some traditional driving jobs may disappear. But AV growth is already creating new career opportunities in:
- Fleet operations and dispatch
- AV software engineering
- Cybersecurity and risk management
- Lidar and sensor manufacturing
- Legal and insurance roles specific to AVs
Vocational training programs are adapting, and companies like Aurora and Waymo have launched AV technician certification programs.
Data Privacy: Who’s Watching You?
Robotaxis are loaded with sensors and cameras — but that data has to go somewhere.
- Waymo states that personal data is anonymized
- Tesla stores real-world driving data to train its neural networks
- Uber and Waabi use ride analytics to improve service areas
Concerns still exist over video recordings inside the cabin, location tracking, and data sharing with third parties. Consumers should review privacy policies and opt-out options if available.
You Can Live Outside the U.S. and Still Collect Social Security — Here’s How
Why 2026 Could Change Retirement Plans Across the U.S.
Who Qualifies for the First U.S. Program Offering $500 Guaranteed Monthly Income?
















